How To Bring Out The Best In Your Middle Performers
This article originally appeared on Forbes by Mark Murphy, Founder of Leadership IQ
There’s a common assumption that middle performers are universally maxed out, already operating at peak efficiency, and with no hope of improvement. It’s a big reason why so many middle performers (who often make up roughly 70% of the workforce) get the least amount of performance coaching from leaders. But only a scant 10% of middle performers actually fall into the maxed out/no hope category. Four very different issues block the remaining 90% from reaching greater potential. And with some focused coaching, these blocks can usually be overcome.
Lack of confidence blocks about 20% of middle performers. For whatever reason, perhaps life history, the way they’re being managed, etc., these middle performers just don’t believe that a greater level of performance is possible for them. They may have the talent, the skills and the right attitude; they just don’t have the confidence. These folks require coaching that pushes them outside their comfort zone so they see just what they really can do.
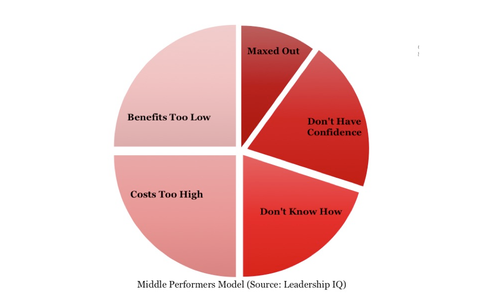
Another group of middle performers simply don’t know how to achieve higher levels of performance. Ask these folks to name the criteria required to be a high performer and you’ll hear lots of off-target responses such as, “high performers went to a certain school,” or “high performers came up on XYZ career path,” or “high performers work overtime and put in lots of late nights.” About 20% of middle performers lack a clear understanding of the criteria to be a high performer. But spell it out by setting clear performance expectations that let these middle performers know exactly what high, low and middle performance looks like, and their performance will improve.
The remaining 50% of middle performers are blocked by two issues that while similar, have subtle differences. There is the costs too high category of middle performer that looks at your high performers and says, “Being a high performer is a miserable existence. High performers work all weekend, are constantly pulling all-nighters and they volunteer for every shift known to mankind. It’s an awful job and I’m not willing to pay that price.” Getting the costs too high folks on track requires identifying their demotivators and taking action where you can to make high performer existence more palatable.
And then there is the benefits too low category of middle performers. We see these folks exert high-performer levels of energy on work that interests and benefits them. But work that isn’t particularly fulfilling, that doesn’t excite and inspire them, doesn’t incent them to give very much. Coaching these benefits too low middle performers to higher performance requires finding opportunities that put them in situations where they see the upside of higher performance.
Diagnosing the blocks that keep middle performers from higher performance requires a five-part conversation. It’s an easy script to follow that prompts middle performers to tell you in their own words what makes them tick and what exactly it will take to help them maximize their potential. Conduct this casual, 15-minute, one-on-one conversation with each middle performer every couple of months.
Part One: Set the stage: “Sarah/Frank, I want to tell you that your performance has been very solid, successfully meeting all expectations. But I also want to tell you that I believe you have untapped potential. I’ve gotten a sense of how talented you are, and I’d like to talk about finding ways to tap that potential. Is this a conversation you feel OK having?”
- “YES” (continue to Part Two)
- “NO” (turn it into a “Yes” by asking: “Do you mind if I ask why?”)
Part Two: Assess their confidence: “Do you see the same potential in yourself that I see in you?”
- “YES” (continue to Part Three)
- “NO” (turn it to a “Yes” by asking: “Do you mind if I ask why?”)
Part Three: Assess their clarity of expectations: “Can you tell me about what you consider to be the criteria for being considered a high performer at this organization?”
Part Four: Assess their perceived costs: “Sometimes when someone has untapped potential, there’s something going on that’s holding them back or demotivating them. Is there anything like that here?” “Can you tell me about a time in the past three (or six or 12) months when you felt particularly demotivated / frustrated / emotionally burnt out?”
Part Five: Assess their perceived benefits: “Sometimes when someone has untapped potential, it feels like it’s not really going to improve your job satisfaction to tap that potential. So let me ask you a question. I know this is a tough one to remember back on, and it probably sounds like it’s out of left field, but give it a shot: When you started in this job, what was your greatest hope? What did you want to achieve or get out of this job? In the past three (or six or 12) months, what’s been your favorite part of the job? Can you tell me more about that? What’s the part of your job that you really look forward to? What was it that really drove you? What did you want to get? What were your aspirations?”
The return on taking the time to maximize your middle performers is incredibly high. You may not always find your next Steph Curry or Serena Williams, but you will elevate their performance and they will give you greater effort, greater diligence and greater time.
Mark Murphy is a NY Times bestseller, author of Hiring For Attitude, and founder ofLeadership IQ.







